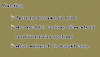BODY TISSUES :
DEFINITION:
Tissue is an aggregation of similar cells and their products that perform same function.
There are four principal types of tissues in the body:
epithelial tissue:
covers body surfaces, lines body cavities and ducts and forms glands
connective tissue:
binds, supports, and protects body parts
muscle tissue:
produce body and organ movements
nervous tissue:
initiates and transmits nerve impulses from one body part to another
EPITHELIAL TISSUES
Perform diverse functions of protection, absorption, excretion and secretion
STRUCTURAL ANATOMY:
Epithelium rests on connective tissue.ž žBetween the epithelium and connective tissue is present the basement membrane which is extracellular matrix made up of protein fibers and carbohydrates.
Basement membrane attach epithelium to connective tissue and also regulate movement of material between epithelium and connective tissue
Epithelial cells are bound together by specialized connections in the plasma membranes called intercellular junctions . There are four types of junctions:
Tight junctions
Present on apical surface and completely attaches each cell to its neighbors.
Formed by fusion of plasma membrane
proteins among neighboring cells so
the apical surfaces of the cells are
tightly connected.
As a result intercellular space is sealed
off
The tight junction forces almost all
materials to move through, rather than
between, the epithelial cells in order
to cross the epithelium.
Adhering junctions
Made up of dense layer of proteins on the inside of the plasma
membrane Transmembrane proteins called cadherin join the cells together.Cadherin are inserted into the protein plaque on in adjacent cells and they join together in the intercellular space.
Adherens junctions help epithelial surfaces resist separation during various contractile activities
Allows passage of material between adjacent cells through lateral surfaces.
Desmosomes
Made up of protein plaque and transmembrane protein that extend into the intercellular space between adjacent cell membranes and attach cells to one another.The protein plaque is attached to elements of the cytoskeleton known as intermediate filaments.
Gap junctions
Gap junctions are made up of tiny fluid filled tunnels called
connexons. Each connexon consists of six transmembrane proteins called
connexin , arranged in a circular fashion to form a tiny, fluid-filled
tunnel or pore At gap junction the cell membranes of adjacent cells are
separated by small intercellular space, as against other types of
junctions where the membranes are fused. Through the gap junctions ions and
small molecules can diffuse from the cytosol of one cell to another,
but the passage of large molecules is prevented.
FUNCTIONS OF EPITHELIAL TISSUES :
Protection:
Selective permeability : in GIT facilitate absorption, in kidney facilitate filtration, in lungs facilitate diffusion.
Secretions : glandular epithelium form linings of various glands, involved in secretions.
Sensations: contain some nerve endings to detect changes in the external environment at their surface
CHARACTERISTICS OF EPITHELIAL TISSUES:
Highly cellular with low extracellular matrix
Polar – has an apical surface exposed to external environment or body cavity, basal layer attached to underlying connective tissue by basement membrane and lateral surfaces attached to each other by intercellular junctions
Innervated
Avascular – almost all epithelia are devoid of blood vessels, obtain nutrients by diffusion
High regeneration capacity