DIVISIONS OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
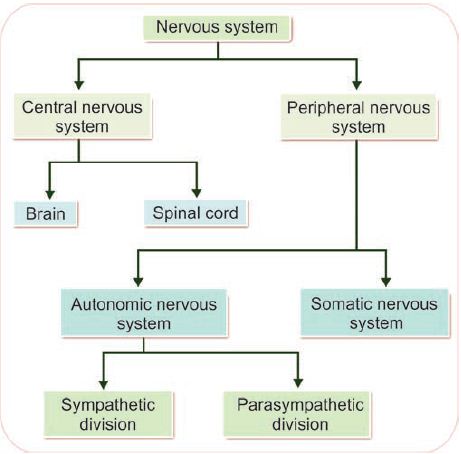
Nervous system controls all the activities of the body. It is quicker than other control system in the body, namely endocrine system. Primarily, nervous system is divided into two parts:
1. Central nervous system
Central
nervous system (CNS) includes brain and spinal
cord. It is formed by neurons and
supporting cells called neuroglia. Structures
of brain and spinal cord are arranged in two
layers, namely gray matter and white matter. Gray matter is formed by nerve cell bodies and the proximal parts of nerve fibers, arising from nerve cell body. White matter is formed by remaining parts of nerve fibers. In brain, white matter is placed in the inner part
and gray matter is placed in the outer
part. In spinal cord, white matter is in the outer part and gray matter is in the inner
part. Brain is situated in the skull. It is
continued as spinal
cord in the vertebral
canal through the foramen magnum of the skull bone. Brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three layers of meninges called
the outer dura mater, middle arachnoid mater and inner
pia mater. The space between arachnoid
mater and pia mater is known as subarachnoid
space. This space is filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid. Brain and spinal cord are
actually suspended in the cerebrospinal
fluid. Important parts of brain and segments
of spinal cord are shown in Figure 133.1.
 |
| central nervous system |
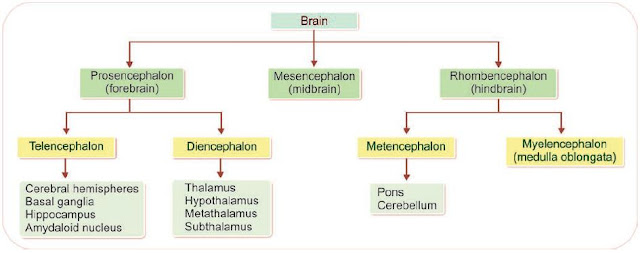
Parts of Brain
Brain
consists of three major divisions:
- Prosencephalon
- Mesencephalon
- Rhombencephalon
1. Prosencephalon
Prosencephalon
is otherwise known as forebrain. It is further divided
into two parts:
i.
Telencephalon which includes cerebral hemispheres, basal ganglia, hippocampus
and amygdaloid
nucleus
ii.
Diencephalon, consisting of thalamus, hypo thalamus, metathalamus and
subthalamus.
2. Mesencephalon
Mesencephalon
is also known as midbrain.
3. Rhombencephalon
Rhombencephalon
or hindbrain is subdivided into two
portions:
i.
Metencephalon, formed by pons and cerebellum
ii.
Myelencephalon or medulla oblongata (Fig. 133.2).
Midbrain,
pons and medulla oblongata are together
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Peripheral
nervous system (PNS) is formed by neurons and their processes present in all
regions of the body. It consists of cranial nerves, arising from brain and spinal
nerves, arising from the spinal cord. It is again divided into two
subdivisions:
1. Somatic nervous system
2. Autonomic nervous system.
1. Somatic Nervous System
Somatic nervous system is concerned with somatic functions. It includes
the nerves supplying the skeletal muscles. Somatic nervous system is
responsible for muscular activities and movements of the body (Fig. 133.3).
2. Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic nervous system is
concerned with regulation of visceral or vegetative functions. So, it is otherwise called vegetative or involuntary nervous system. Autonomic nervous system consists of two divisions, sympathetic division and parasympathetic division.